Location Intelligence (LI) and Business Intelligence (BI) are both very different analytical approaches that organizations use to derive insights from their business data, but they utilize different types of data and can offer very different insights into the health of the business.
Difference Between Location Intelligence and Business Intelligence
Let’s learn the meaning, definition, and key difference between location intelligence and business intelligence.
Business Intelligence
- BI primarily analyzes various business data to help organizations make informed decisions. This includes data related to sales, customer demographics, financial performance, inventory levels, and more.
- BI tools and techniques often involve querying structured data from databases, generating reports, creating dashboards, and employing data visualization techniques to represent insights.
- BI aims to improve operational efficiency, identify trends, optimize processes, and ultimately enhance business performance.
Location Intelligence
- LI focuses specifically on leveraging spatial data and geographic information systems (GIS) to understand patterns and trends related to location.
- It involves analyzing data with spatial components such as physical addresses, geo-coordinates, boundaries, or other location-based attributes.
- LI can provide insights into demographics, market analysis, site selection, logistics optimization, risk assessment, and more by incorporating spatial context into decision-making processes.
- LI often uses GIS software to visualize spatial data, perform spatial analysis, and derive meaningful insights.
- Most importantly, leaders must rely on location intelligence to streamline and orchestrate successful field operations.
Key Differences
- Data Focus
BI deals with a broad range of business data, including non-spatial data, while LI specifically focuses on spatial data.
- Use Cases
BI is used for various business analytics like sales forecasting, customer segmentation, and financial analysis. LI is used for location-specific analyses such as territory planning, store location optimization, and route optimization.
- Insights
While both BI and LI aim to provide insights, the nature of insights differs. BI provides insights into business operations and performance, while LI provides insights into geospatial patterns, trends, and geospatial insights.
In the context of assessing decision-making insights for organizations with heavy field operations like outside sales, field servicing for customers, delivery operations, managing supply chain, and others, Location Intelligence is imperative.
The right location intelligence software can help optimize workflows, enhance efficiency, and drive strategic decision-making.
Harness the Power of Location Intelligence
1. Geospatial Contextualization
Location Intelligence excels in providing spatial contextualization, allowing field operations managers to visualize data within its geographic context. Whether it’s optimizing vehicle routes, managing field workforce, or identifying service areas, LI empowers decision-makers to understand their entire lay of land and run their operations successfully.
By overlaying data onto maps, field managers gain a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships between their field staff, partners/dealers, customers, and even competitors.
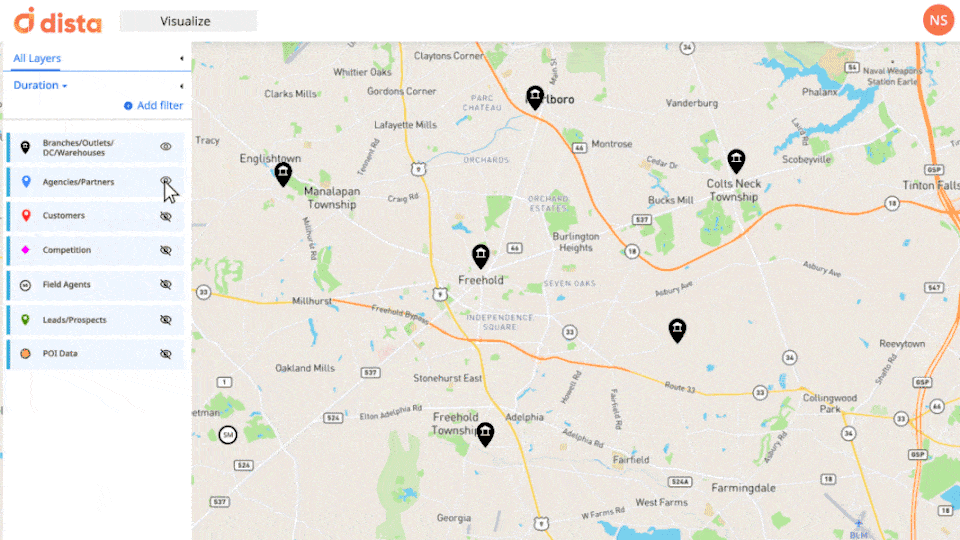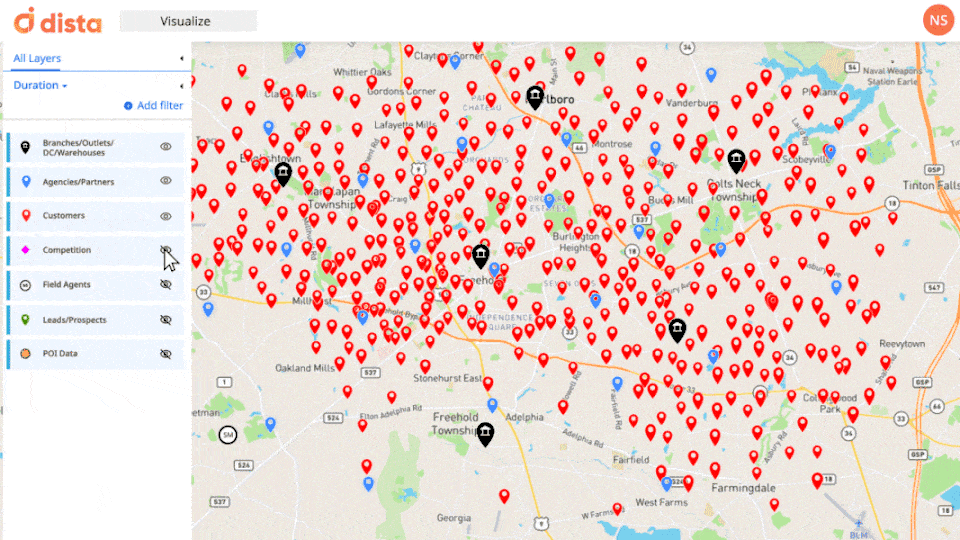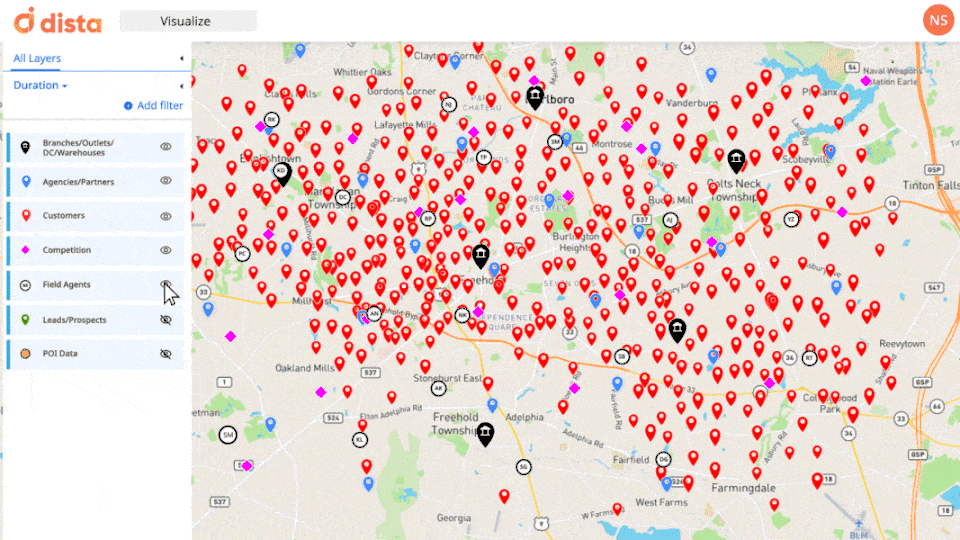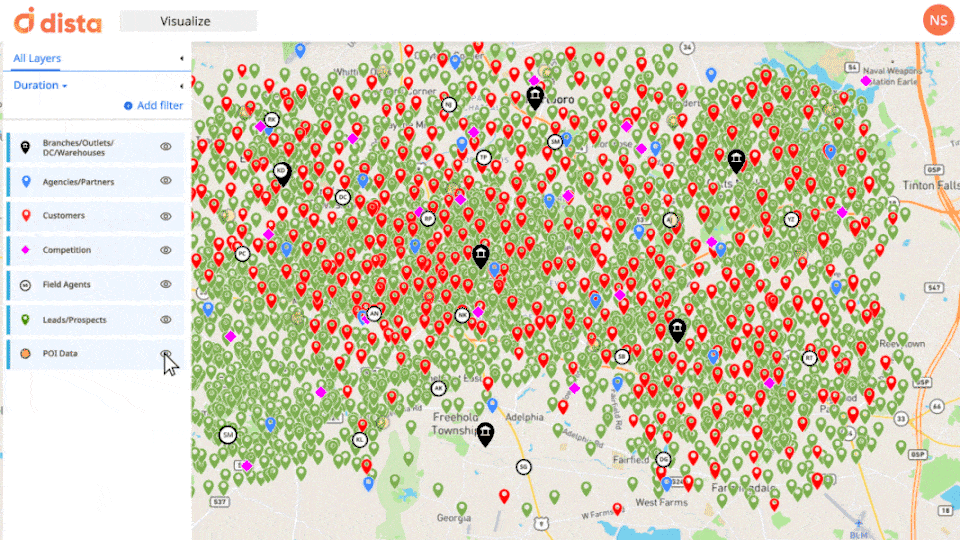
2. Real-time Monitoring, Analysis, and Actioning
Field operations demand real-time monitoring and analysis to respond to dynamic situations and optimize resource allocation promptly. LI leverages geospatial technologies to collect, analyze, and visualize data in real-time, driving agile decision-making, and implementing it in the field leading to improved efficiency.
See how a location intelligence platform can help you visualize, strategize, and operationalize your entire field operations.
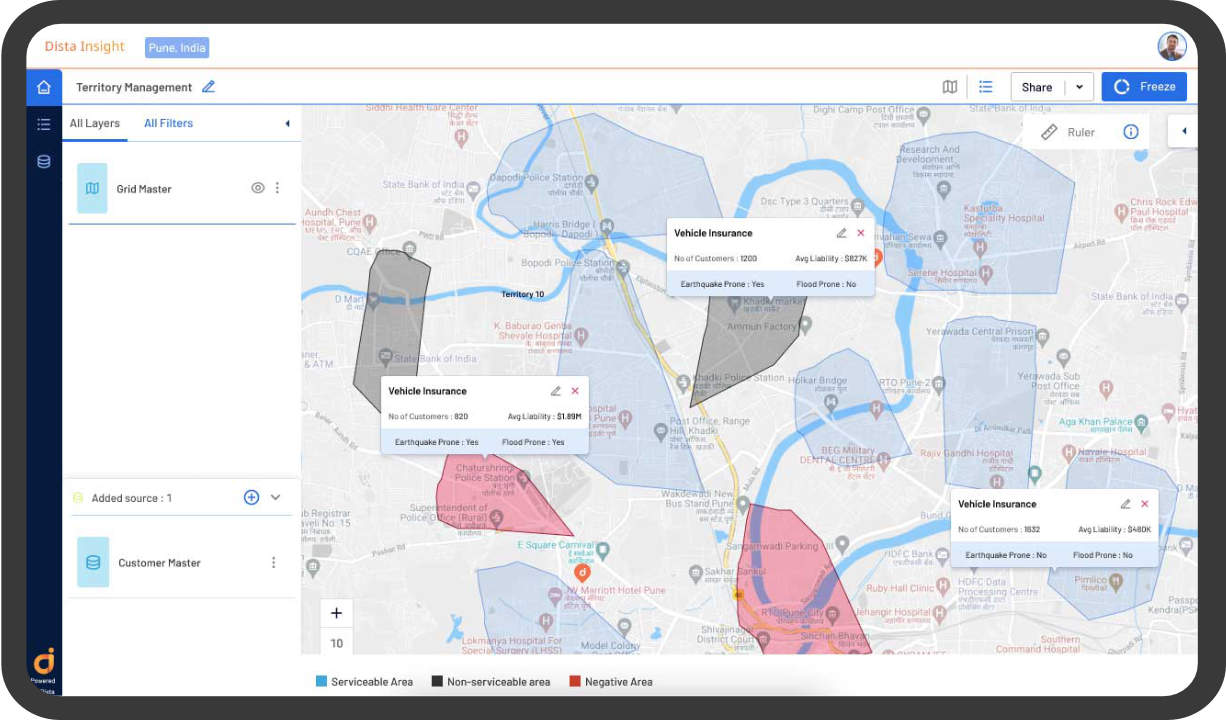
3. Geospatial Optimization for Territory Management
Efficient routing, resource allocation, and workload distribution are critical components of territory management. LI offers advanced spatial optimization capabilities that outpace traditional BI approaches. LI optimizes routes, schedules, and enterprise workflows through geospatial algorithms and predictive modeling to minimize travel time, reduce fuel consumption, and enhance overall productivity.
LI ensures that field operations are executed with maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness by factoring in spatial constraints such as traffic patterns and proximity to customers. Sophisticated software like Dista employs tried and tested frameworks factoring in 100+ business constraints like skillset of the field resource, the capacity of their workload, and priority of work, among others.
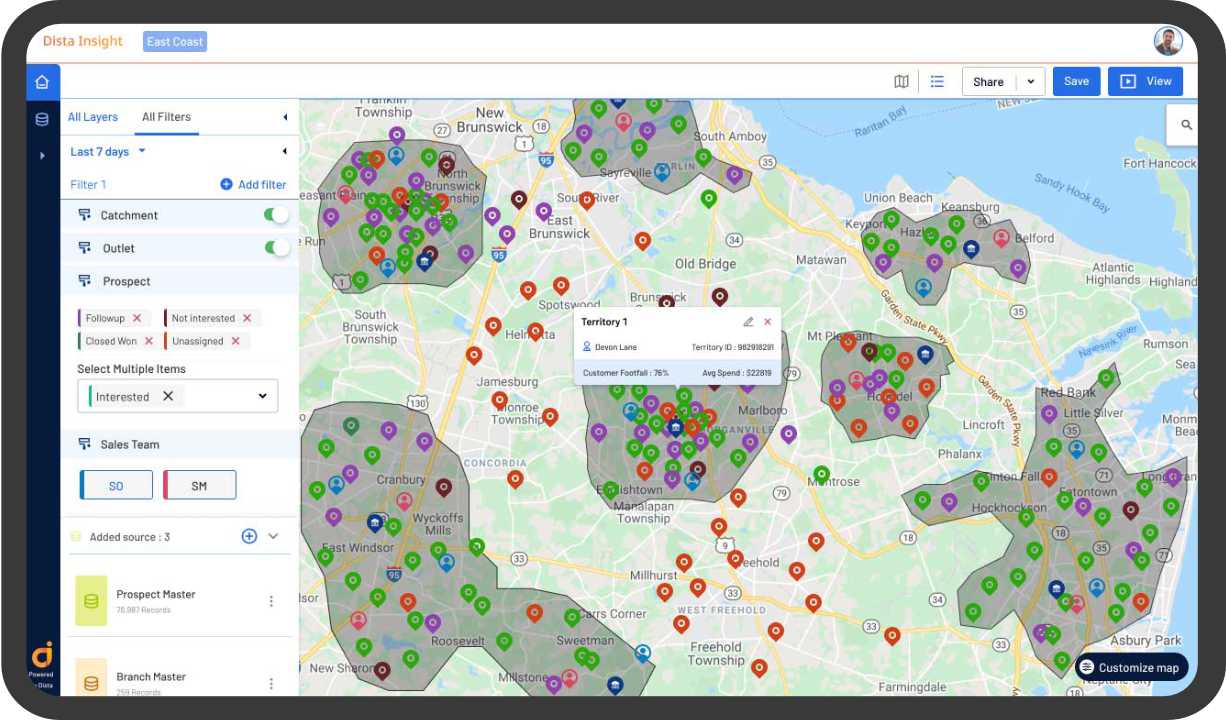
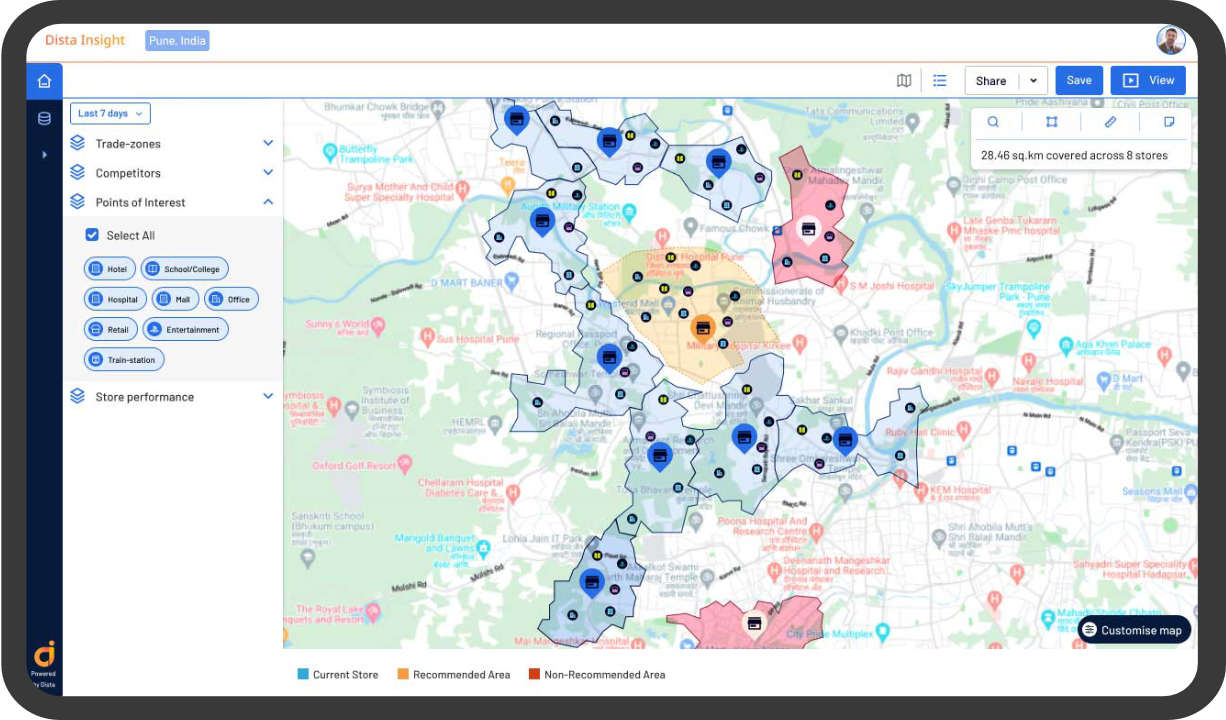
4. Site Selection and Planning
For industries like retail, banks, telecommunications, and infrastructure development, site selection plays a pivotal role in the success of field operations. Location Intelligence equips decision-makers with spatial analytics tools that facilitate comprehensive site evaluation, considering factors such as demographics, market demand, accessibility, and competitor presence.
By conducting spatial analysis and modeling, LI enables organizations to identify optimal site locations, mitigate risks, and capitalize on market opportunities with precision and foresight.
5. Geospatial Risk Analysis
Location Intelligence also provides indispensable support for risk assessment leveraging spatial data and demographics to identify vulnerable areas, high-risk markets, and more. Businesses are able to identify fraudulent behavior and suspicious activity faster using geospatial insights.
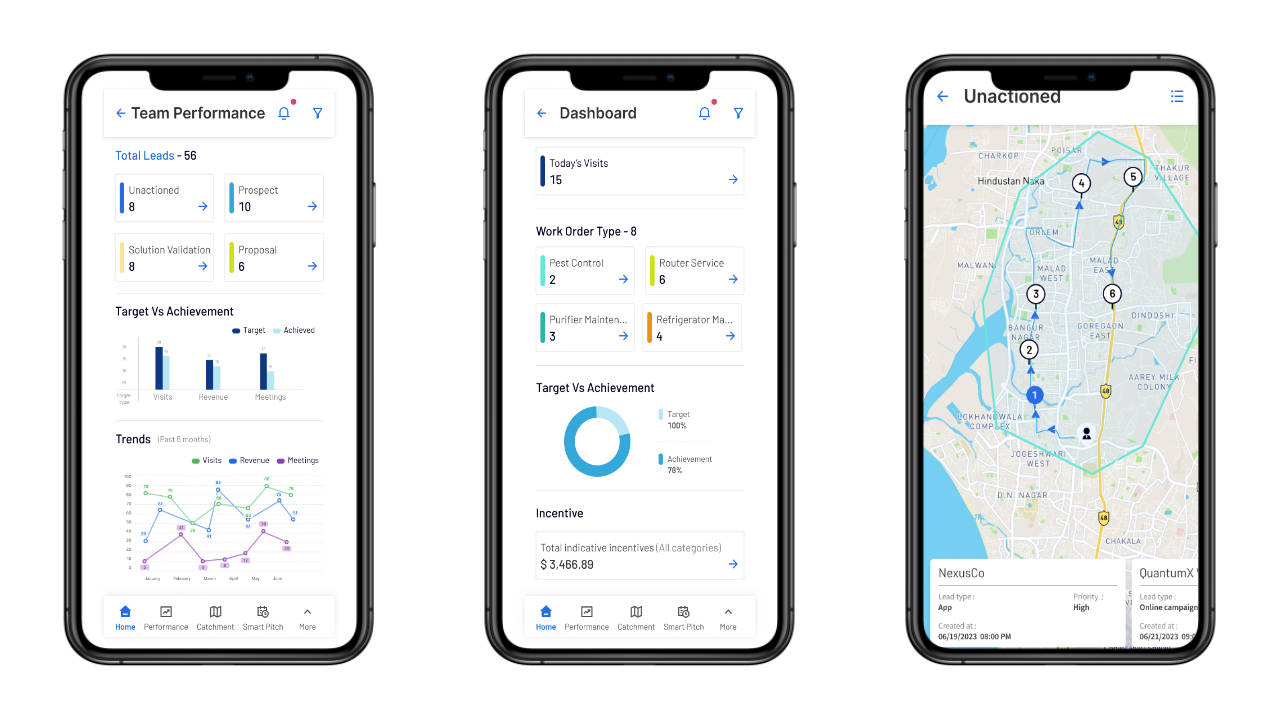
6. Seamless Field Orchestration with Mobile Integrations
Field operations increasingly rely on mobile technologies to collect data and communicate with prospects. Location intelligence software like Dista Sales, Dista Service, and Dista Deliver seamlessly integrates with these hand-held devices, enabling organizations to harness the power of location-aware devices for data collection, workflow orchestration, and workforce management.
By leveraging location-based services and spatially enabled mobile applications, LI enhances situational awareness, facilitates seamless collaboration, and empowers field personnel to make informed decisions on the go.
In the dynamic landscape of field operations, Location Intelligence emerges as a transformative technology, offering unparalleled capabilities for geospatial analysis, real-time monitoring, and strategic decision-making.
While Business Intelligence remains a valuable tool for analyzing structured data, Location Intelligence transcends its limitations by providing spatial context, enabling real-time insights, and facilitating geospatial optimization. By embracing Location Intelligence, organizations can unlock new opportunities, streamline field operations, and gain a competitive edge.