Geographic Information System (GIS) analyze spatial data. A URISA market survey recently stated a significant increase in GIS applications for spatial analysis, map development, and data management. There are several benefits of using GIS tools to improve decision making and enhance operational efficiency.
Enterprises looking to gain a competitive advantage should explore the viability of GIS in daily operations. Simultaneously, they should focus on the ever-evolving trends shaping the outlook for GIS applications in 2024.
Also Read: 7 Ways GIS Can Improve Your Business
Here are the top GIS trends businesses are expected to adopt in 2024 for better strategic decision-making.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) and GIS
GIS and IoT share a powerful synergy where GIS integrates spatial data with IoT devices. These technologies combined provide spatial context for businesses. The integration helps enhance data analysis, provide actionable insights, and improve decision-making for enterprises.
For example, in a use case like smart city planning, a wide range of interconnected IoT devices can monitor real-time traffic flow. GIS will analyze this data and optimize traffic management. Similarly, IoT devices can monitor the air quality for a particular location. GIS can analyze this data to optimize infrastructure to lower carbon footprint.
Another scenario is IoT devices collecting energy consumption data for a particular region. GIS can research and provide key insights, enabling business managers to develop strategies for urban sustainability.
2. Market Expansion
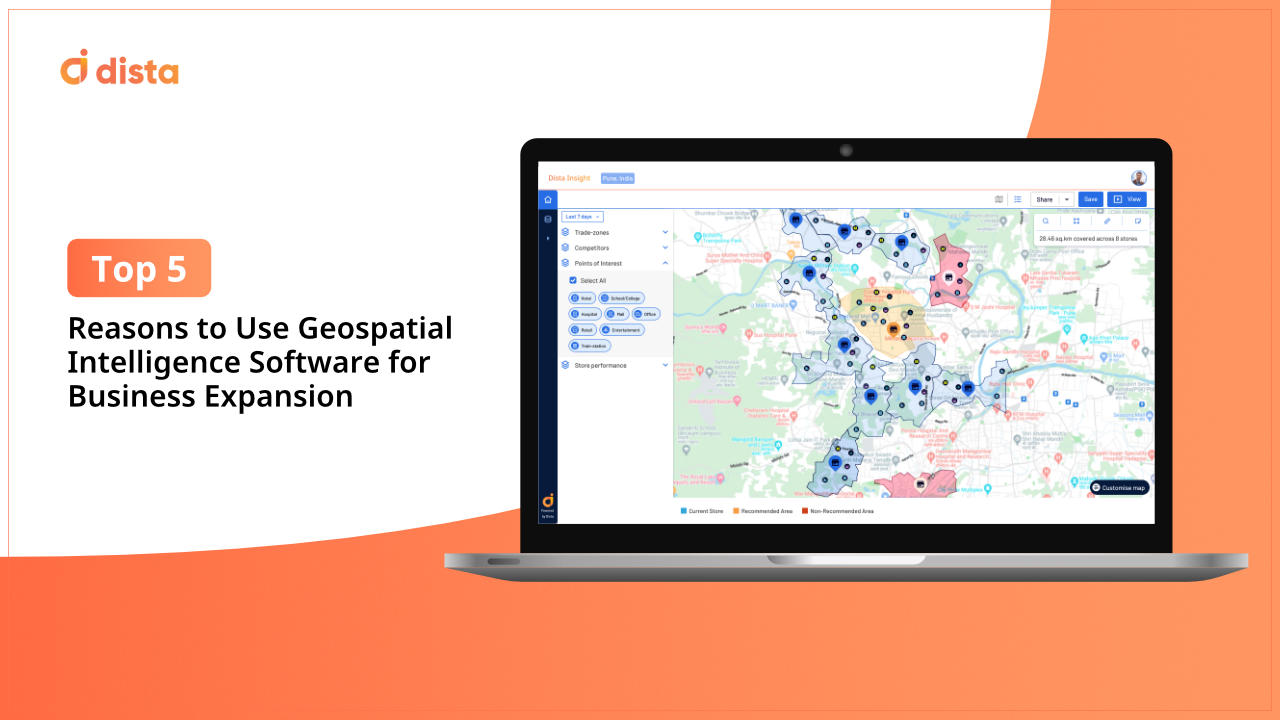
GIS technology can provide a detailed market analysis. Businesses can assess demographic data points, monitor consumer behavior, and track socio-economic factors. GIS provides relevant spatial context to this market data, allowing different types of businesses to visualize, analyze, and interpret geographic information.
A retail store wants to optimize its store locations and open new outlets. GIS technology helps gather relevant customer demographic data, market demand, and POI data and analyzes competition in the target area.
It performs spatial analysis to assess higher footfall for the brand in new locations. This way, the outlet will know where to place their best stores and increase brand visibility. Strategic placement of new stores is optimized using location intelligence. This improves customer engagement and increases profitability.
3. GIS Risk Analysis
A thorough business risk assessment identifies possible scenarios that affect its stability or profitability. Take the example of financial institutions. By leveraging GIS technology, financial institutions can achieve a more sophisticated and location-aware understanding of the risks.
Banks analyze collective geospatial data to map out negative impact areas. This level of visualization enables better risk assessment. Businesses can map out delinquency trends and assess customer credit profiles by location.
4. Smart Urban Planning
GIS technology can analyze spatial data points combined with complex data sets. This integration is especially beneficial for urban planning and real estate development.
Using GIS, urban planners and real estate developers can create a map to visualize population distribution, land use, transportation networks, environmental impact, and infrastructure management. Planners can assess the scope of projects with this improved visibility.
GIS software can help map zones and allocate land for different construction projects. It can even assess the environmental impact of planned projects and check whether there is scope for sustainable development.
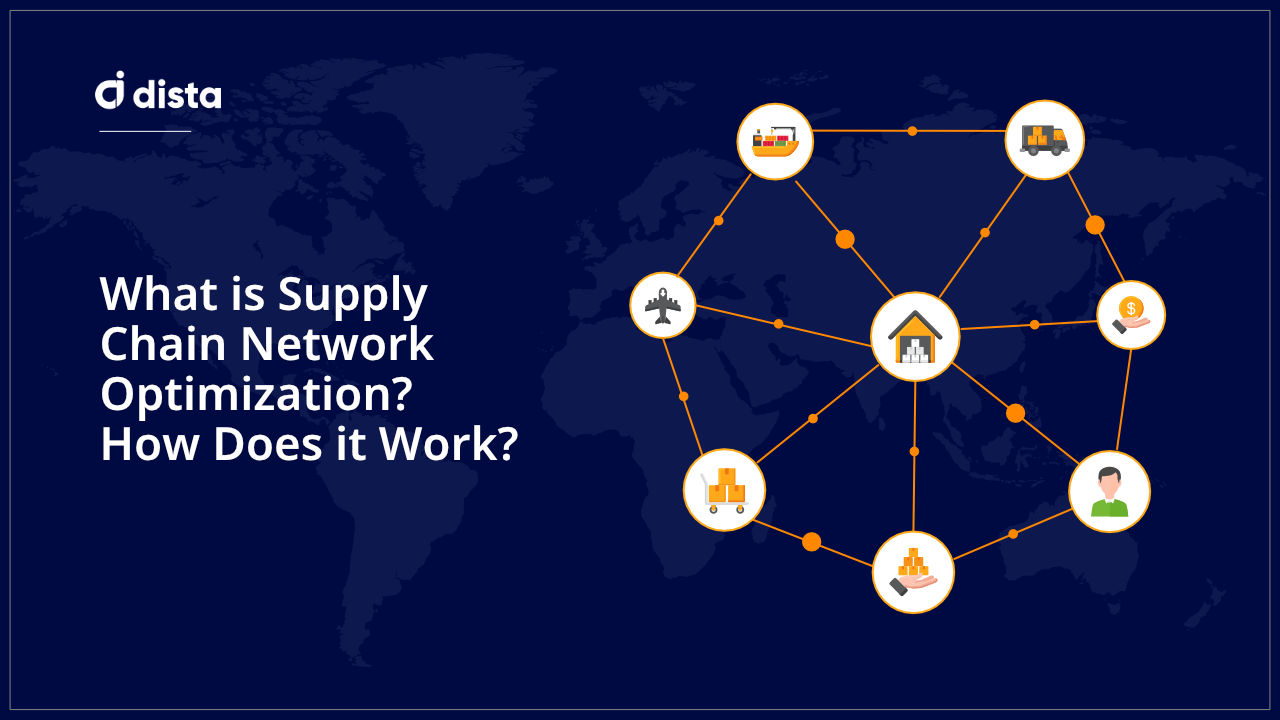
5. Supply Chain Management
Planning, sourcing, manufacturing, logistics, and returns are vital elements that define supply chain management. It is a complex process that poses challenges like predicting consumer demand, managing delivery costs, logistics, resources management, and long lead times.
Supply chain managers can apply GIS technology to enhance their daily operations. It helps:
- Provide spatial analysis for site selection
- Enable route optimization and logistics planning
- Improve inventory management with demand forecasting
- Enable risk assessment within supply chain networks
- Improve partner collaboration and stakeholder satisfaction
GIS mapping improves visibility for managers to locate and choose suitable warehouse locations. It also minimizes commuting distance for scheduled deliveries and improves quick commerce. The resulting benefit is lower fuel consumption and transportation costs for managing multiple deliveries.
Leveraging GIS tools enables organizations to unlock the full potential of their supply chains.
6. Cloud Computing and GIS
GIS on a cloud platform is one of the emerging trends to look out for in 2024. The adoption of GIS as a service is increasing rapidly due to the introduction of GIS software.
One significant benefit of embracing cloud technology is that businesses can scale their operations without investing in hardware or new infrastructure. GIS features can be accessed virtually on the cloud platform by multiple users.
The convergence of cloud computing and GIS offers a more cost-effective solution for businesses. It helps companies streamline their real-time operations using public, private, or hybrid GIS cloud services. Users can access all relevant data managed and updated on a cloud platform.
7. Emergency Management using GIS
Location data plays a crucial role in assessing vulnerabilities and risk factors for a particular region. GIS can provide real-time location data, meteorological data, sensor data, and feeds from social media. This information improves preparedness and emergency response for various calamities.
Here are some ways GIS tools help supplement emergency response management:
- Create a Visual Map
GIS helps create a visual map of hazard zones or highlight hotspots to improve the overall visibility of a potential calamity. Spatial analysis makes it easier for decision-makers to prioritize these geographic locations and create a comprehensive risk profile.
- Risk Assessment
GIS enables better assessment of vulnerabilities by mapping geographical areas and assessing potential risk impact.
- Resource Allocation
Mapping the location of emergency shelters, medical facilities, or emergency supplies optimizes the process of resource allocation during an actual emergency.
Using GIS technology, emergency response managers can analyze high-risk areas, simulate scenarios to improve emergency response, and better manage natural emergency risk.
Final Thoughts
Integrating GIS tools has become more than just a necessity for enterprises looking to gain a competitive advantage. The technology has a transformative impact that enhances business operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and delivers superior customer experiences.
Would you like to learn more about our GIS software? Get in touch with us now.